Write It Right: Documentation and authorization requirements for automotive repair dealers
Updated January 2026
Automotive repair dealers must comply with the Automotive Repair Act and related laws and regulations. This includes documentation and authorization requirements for repair transactions, such as:
Keeping the customer informed
Providing estimates and invoices to the customer
Performing only the repairs authorized by the customer
Maintaining a record of all repairs performed and parts supplied
Write It Right is a resource to help you meet these and other requirements. Note that this information is for quick-reference purposes only and is not all-inclusive. Statutory and regulatory references are included. To learn more, see Laws and regulations.
BPC refers to Business and Professions Code. HSC refers to Health and Safety Code. CCR refers to California Code of Regulations.
Estimate
An estimate is a paper or electronic document provided to the customer that contains an estimated price for parts and labor for a specific job. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3352(a))
Unless specified otherwise, all references to the estimate are intended for a ‘standard’ repair estimate.
When is an estimate required?
An estimate is required for an automotive repair dealer to perform repairs to a motor vehicle. (BPC § 9884.9)
When is an estimate not required?
An estimate is not required for an automotive repair dealer to perform any of the preventative maintenance services defined in BPC § 9880.1(j) if the customer authorizes the service and either of the following occur:
The service is performed free of charge. (BPC § 9884.9(e)(1))
The total price for parts and labor necessary to perform the service is displayed in a conspicuous manner or is made available to and acknowledged by the customer. (BPC § 9884.9(e)(2))
If a job involves both repairs and preventative maintenance services, an estimate is required to perform the repairs. Although not required, it is best practice to list the preventative maintenance services on the estimate. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353(a))
What is required in an estimate?
An estimate must contain a description of the specific job and the estimated price for all parts and labor. Each part listed in the estimate shall be new unless specifically identified as a used, rebuilt, or reconditioned part. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353(a))
Is sales tax included in the estimate?
No, sales tax is only included in the invoice. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(5))
Are toxic waste disposal costs included in the estimate?
Yes, any charges associated with the handling, management, and disposal costs of toxic wastes or hazardous substances directly related to the specific job must be itemized separately in both the estimate and the invoice. If a disposal fee is charged, the estimate and invoice also must both include the automotive repair dealer’s Environmental Protection Agency identification number. (BPC §§ 9884.8, 9884.9(a), CCR § 3357)
Is the labor rate included in the estimate?
No, the labor rate is not included in either the estimate or the invoice. However, vehicle safety systems inspection stations must post conspicuously the price for a vehicle safety systems inspection. Additionally, Smog Check stations must post conspicuously a list of prices for their services and an hourly labor rate for repairs. (CCR §§ 3312.2(d), 3340.15(d))
Can the customer be charged for shop supplies?
No. Charging for items generally noted as shop supplies or miscellaneous parts is prohibited. The customer may only be charged for the supplies used on their vehicle. The cost of these supplies must be included as part of the estimate and all supplies must be itemized in the invoice. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3356(g))
If the customer requests the return of replaced parts, is it included in the estimate?
Yes, if the customer requests the replaced parts at the time the estimate is authorized. (BPC § 9884.10, CCR §§ 3355, 3356(i))
Are core charges on parts included in the estimate?
If a customer requests a replaced core part (such as a battery) that is sold on an exchange basis, the core charge may be included in the estimate. Note that core charges on parts do not apply to parts replaced under a warranty, which must be returned to the manufacturer. (BPC § 9884.10, CCR §§ 3355, 3356(i))
Can repairs be sublet? Who is responsible for the sublet repairs?
Yes, sublet repairs can be performed with the consent of the customer. The automotive repair dealer must include with the estimate a statement of any sublet repair to be performed on the vehicle. The automotive repair dealer is responsible for all sublet repairs in the same manner as if it had performed the repairs. At the request of the customer, the name and location of the facility performing the sublet repairs must be disclosed. (BPC §§ 9884.7(a)(9), 9884.9(b), CCR § 3353(f))
Can Smog Check inspections and/or repairs be sublet?
Smog Check inspections cannot be sublet. (CCR § 3340.15(h)) However, Smog Check stations performing repairs may sublet the following:
Exhaust systems: Repairs of a vehicle’s exhaust system that are normally performed by muffler shops, provided the malfunction has been previously diagnosed by the Smog Check station originally authorized by the customer to perform repairs to the vehicle. (CCR § 3340.15(h)(1))
Defective components: Repairs of those individual components that have been previously diagnosed as being defective and that have been removed by the Smog Check station originally authorized by the customer to perform repairs to the vehicle. (CCR § 3340.15(h)(2))
Diesel-powered vehicles: Repairs of diesel-powered vehicles, provided the Smog Check station has obtained authorization from the customer to sublet repairs to the vehicle. (CCR § 3340.15(h)(3))
Transmissions: Repairs to a vehicle’s transmission, provided the Smog Check station has obtained authorization from the customer to sublet repairs to the vehicle. (CCR § 3340.15(h)(4))
On-board computer system software: Corrections to the vehicle’s on-board computer system software, provided that the malfunction has been previously diagnosed by the Smog Check station originally authorized by the customer to perform repairs to the vehicle. (CCR § 3340.15(h)(5))
Specialized estimates
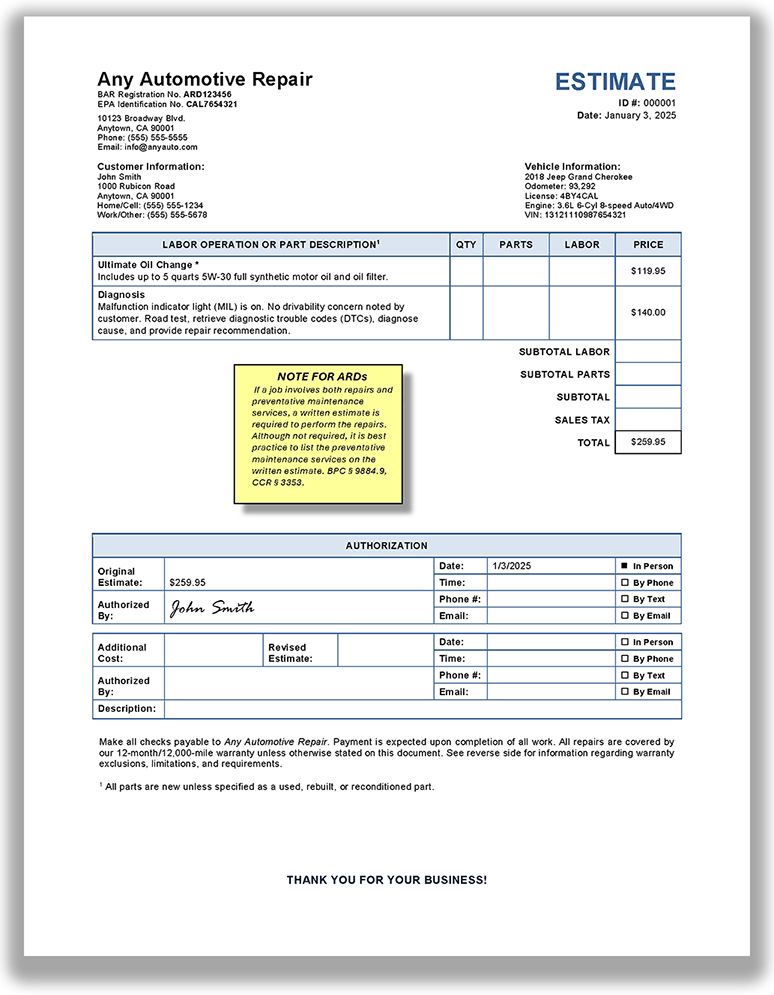
When is a tear down estimate required?
A tear down estimate is required before disassembling a portion(s) or area(s) of the vehicle or vehicle component(s) for diagnosis. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353(c))
What is required in a tear down estimate?
A tear down estimate must contain the same information that is required in a standard estimate, plus the following: (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353)
The cost of the tear down and a description of the portion(s) or area(s) of the vehicle or vehicle component(s) that will be disassembled. (CCR § 3353(c)(1)(A))
Specify the general area of the vehicle that will be disassembled. An itemized list of every part that will be removed during the tear down is not required.
For example, for a front-end collision:
“Front of vehicle” is acceptable.
“Area of damage” is not acceptable.
The cost of reassembling the portion(s) or area(s) of the vehicle or component(s). (CCR § 3353(c)(1)(B))
The cost of all parts and labor necessary to replace items that are normally destroyed by a tear down, such as gaskets, seals, and O rings. (CCR § 3353(c)(1)(C))
Notification that the tear down might prevent the restoration of the vehicle or component(s) to the condition in which it was provided by the customer, if applicable. (CCR § 3353(c)(1)(D))
The maximum time it will take to reassemble the vehicle or component(s) in the event the customer does not want to proceed with the repairs. CCR § 3353(c)(1)(E)
The maximum time is counted from the date of authorization of the tear down. (CCR § 3353(c)(1)(E))
View a sample tear down estimate
Is a second estimate required after the tear down?
Yes. Upon completion of the tear down, the automotive repair dealer must provide the customer an itemized estimate for parts and labor necessary for the required repairs. The automotive repair dealer must then obtain the customer’s authorization to repair or reassemble the vehicle or component(s). (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353(c)(2))
If the customer declines repair or reassembly after a tear down, document that fact in the tear down invoice. (CCR §§ 3353(c)(3), 3356(h))
What is required in a Smog Check estimate?
A Smog Check estimate must contain the same information that is required in a standard estimate, plus the following: (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353)
A test-and-repair station must include a notice stating that the customer may choose another Smog Check station to perform needed repairs, installations, adjustments, or subsequent tests. (HSC § 44033(c))
A test-and-repair station must disclose both orally and in writing in the estimate if the vehicle may be affected by any of the following conditions:
The station does not have adequate equipment, personnel, tools, or reference materials to repair the vehicle, should the vehicle fail its inspection. (CCR § 3340.16.5(b)(1))
The station, as a matter of policy, does not repair certain types, makes, or models of vehicles. (CCR § 3340.16.5(b)(2))
The station, as a matter of policy, does not repair certain types of vehicle inspection failures (e.g., tailpipe, fuel evaporative system, readiness monitors, etc.). (CCR § 3340.16.5(b)(3))
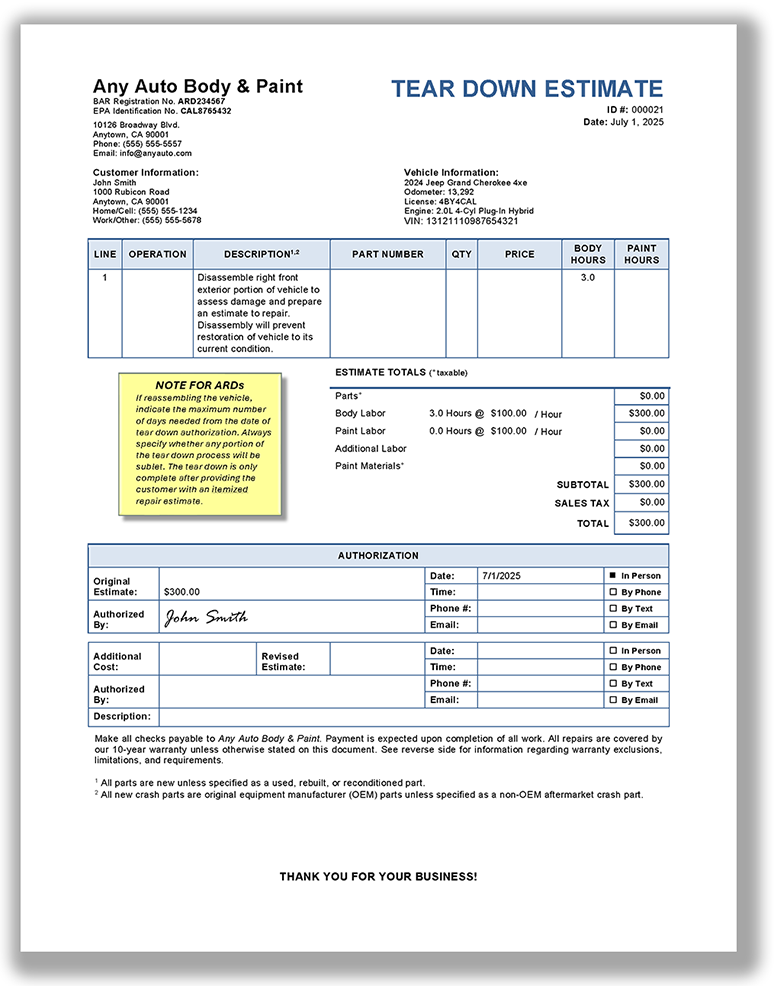
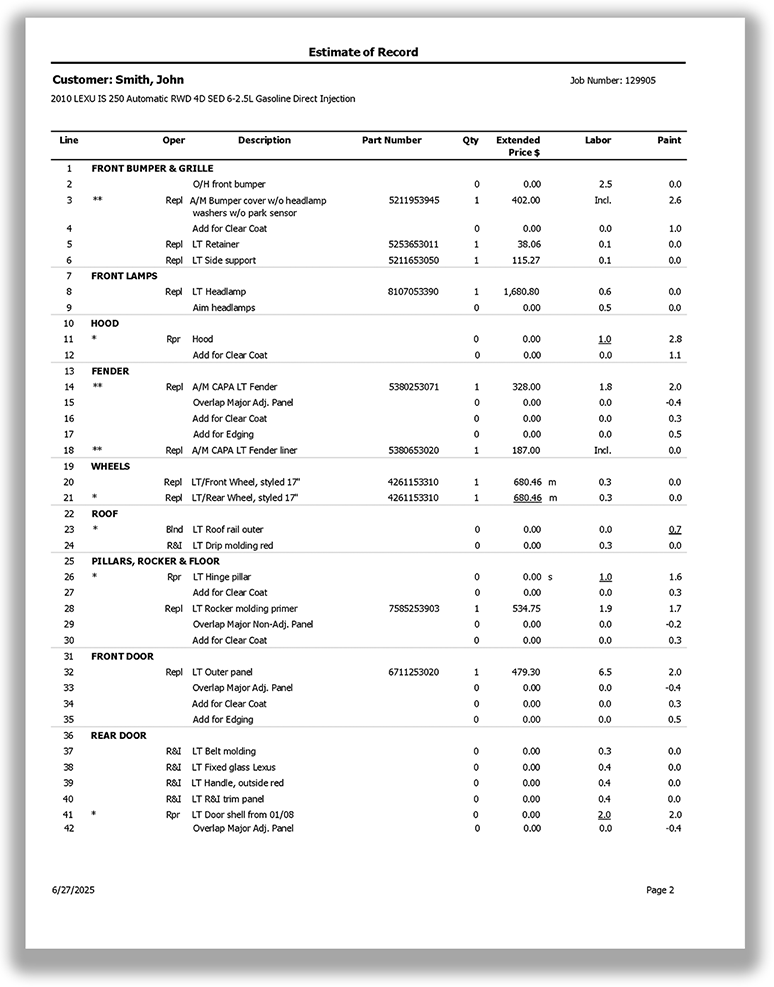
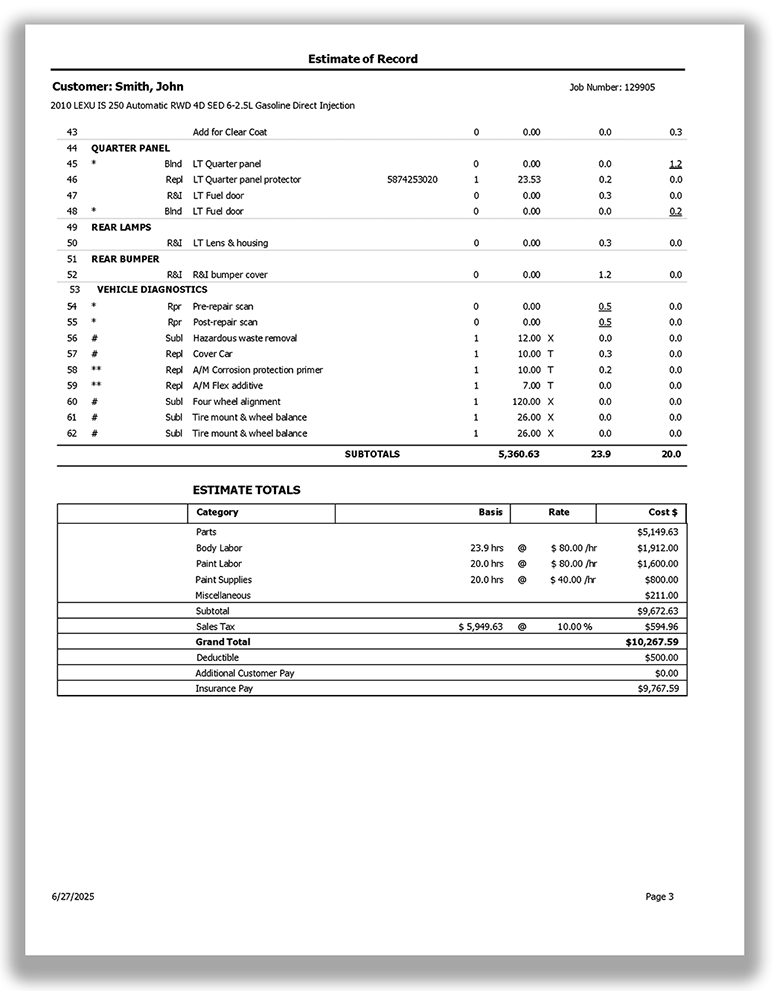
What is required in an auto body or collision repair estimate?
An auto body or collision repair estimate must be itemized and contain the same information that is required in a standard estimate.
In addition, each new replacement crash part listed in an auto body or collision repair estimate must be a new OEM crash part unless specifically identified as a non-OEM aftermarket or used crash part. Terms like Opt-OEM, Alt-OEM, OEM-Surplus, Like Kind Quality, Quality Replacement Part, and similar designations do not satisfy this requirement. (BPC §§ 9884.8, 9884.9, CCR §§ 3352(b), 3353)
An estimate provided by an insurance company may be attached to and referenced in the automotive repair dealer’s estimate if it meets all applicable estimate requirements specified in BPC § 9884.9 and CCR § 3353.
View a sample auto body/collision repair estimate
How should paint and materials costs be included in an auto body or collision repair estimate?
There are two common ways to estimate the cost of paint and materials in collision repairs:
Hourly rate – estimates the cost of paint and materials based on an hourly rate for paint operations.
Actual cost – calculating the actual costs for the paint and materials used in the repair.
Both methods are acceptable.
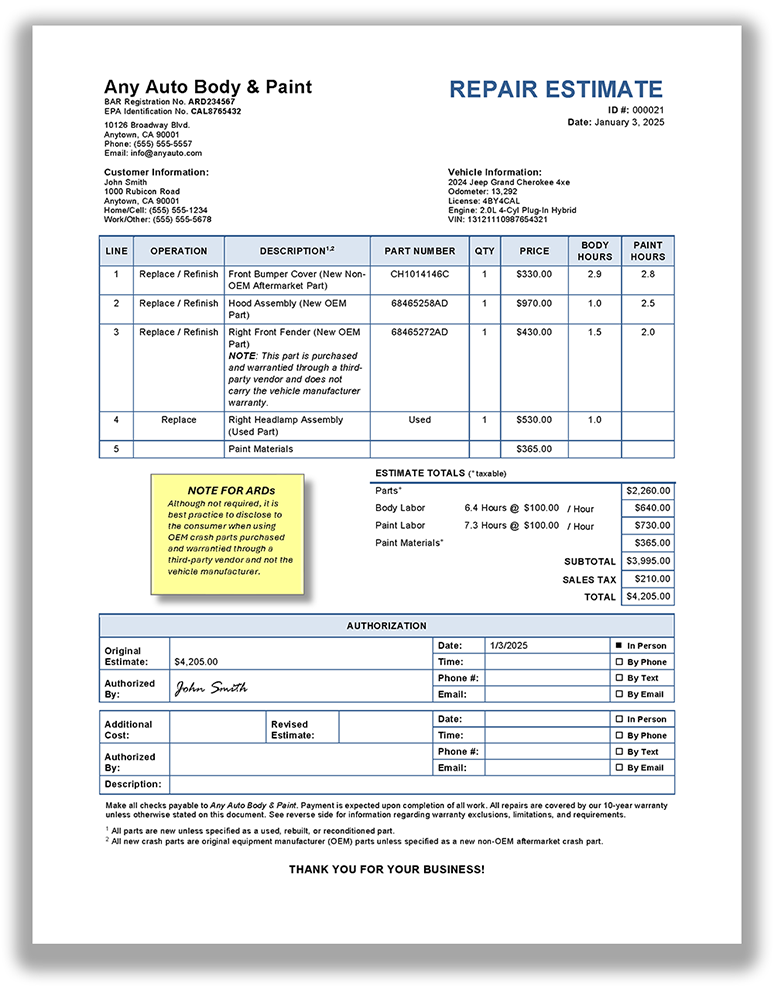
What is required if an automotive repair dealer uses a third-party estimate to create its own estimate?
An automotive repair dealer is encouraged to prepare an estimate based on their own inspection and diagnosis. As an alternative, they may use an estimate prepared by a third-party payor to create their own estimate. If choosing this alternative, the automotive repair dealer must: (CCR § 3353(b)(1))
Notify the customer that the third-party estimate is subject to the California Department of Insurance’s Fair Claims Settlement Practice Regulations. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(A))
Ensure the third-party estimate complies with all applicable requirements in CCR § 3353 and the Business and Professions Code. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(B))
Include on the automotive repair dealer estimate:
A statement that the vehicle will be repaired based on the third-party estimate. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(C)(i))
The name of the third-party payor. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(C)(ii))
The claim number or other unique identifier from the third-party estimate. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(C)(iii))
The total cost of repair listed in the third-party estimate. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(C)(iv))
Attach a copy of the third-party estimate to the automotive repair dealer estimate. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(D))
If the customer authorizes any changes that would alter the cost of repair, notify the third-party payor before performing any repairs. (CCR § 3353(b)(1)(E))
View a sample repair estimate based on a third-party estimate
What is required if an automotive repair dealer accepts payment provided by a third-party payor?
If payment will be provided by the third-party payor, include the payment amount on the automotive repair dealer estimate. (CCR § 3353(d)(1))
If the amount is not known, include the following statement on the automotive repair dealer estimate:
"This estimate is for repairs to meet vehicle manufacturer and industry standards. As the customer, it is your responsibility to contact the third-party payor for approval of payment for the repairs you have authorized." (CCR § 3353(d)(2))
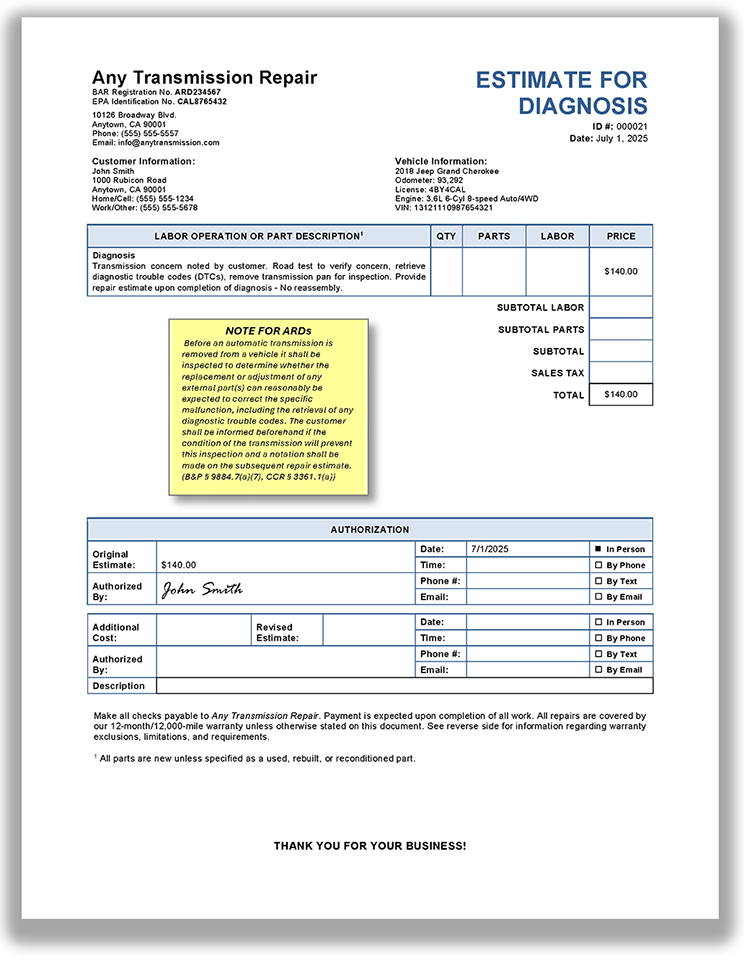
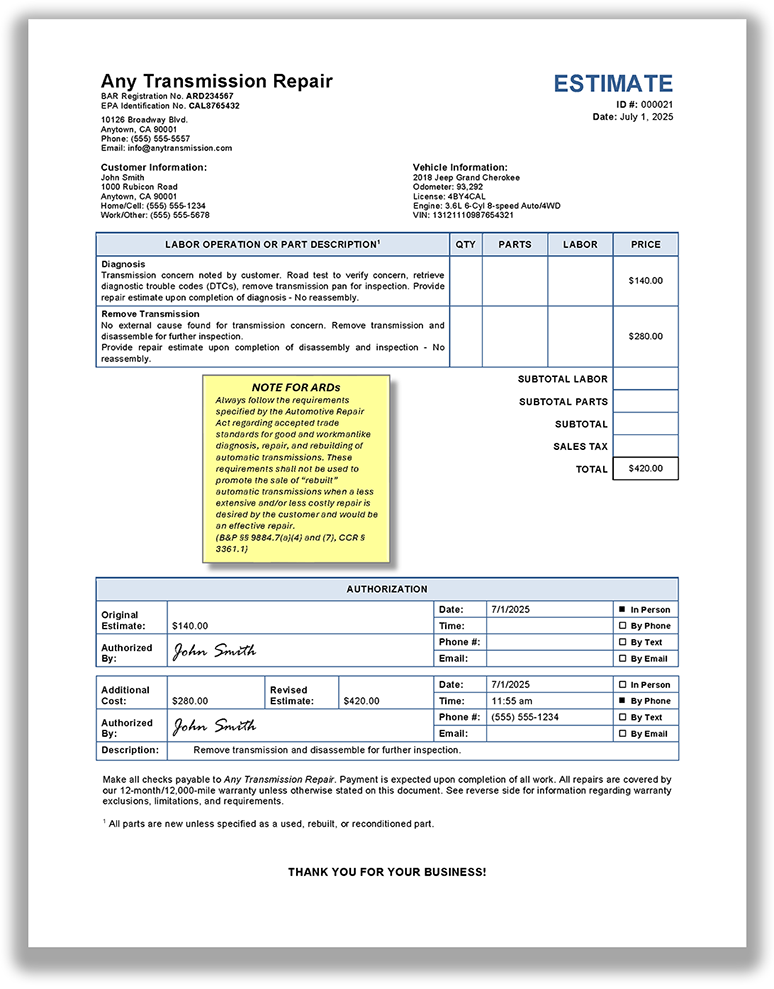
What is required in an automatic transmission estimate?
An automatic transmission estimate must contain the same information that is required in a standard estimate. It also must include notification that a diagnostic check of an electronic control module cannot be completed due to the condition of the automatic transmission, if applicable. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR §§ 3353, 3361.1(a))
Using terms like exchanged, rebuilt, remanufactured, reconditioned, overhauled, or any expression of like meaning, to describe an automatic transmission in an estimate or invoice (or in any form of advertising), is permitted if all work specified in CCR § 3361.1(c) has been completed since the transmission was last used.
View a sample automatic transmission diagnosis estimate
View a sample automatic transmission tear down estimate
What is required in a windshield installation estimate?
A windshield installation estimate must contain the same information that is required in a standard estimate. It also must include whether the windshield is an OEM or non-OEM part and must notify the customer that installation of the windshield will prevent operation of the vehicle for a period of time. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR §§ 3353, 3365.1(c)(3))
What is required in an automotive air conditioning estimate?
An automotive air conditioning estimate must contain the same information that is required in a standard estimate. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353)
When using terms like service, inspection, diagnosis, top off, performance check, or any expression of like meaning, to describe automotive air conditioning work in an estimate or invoice (or in any form of advertising), an automotive repair dealer must perform all procedures specified in CCR § 3366 as the accepted trade standards for air conditioning work.
Authorization
Authorization is the customer’s consent for a specific job, expressed as either:
A written signature on the estimate authorizing a specific job (CCR § 3352(f)(1))
A statement communicated either orally or electronically to the automotive repair dealer and documented on the estimate authorizing a specific job (CCR § 3352(f)(2))
How is authorization obtained?
All repairs must be authorized by the customer in written, oral, or electronic form. The authorization must be obtained and recorded on the estimate before beginning any repairs. The customer must be provided a copy of any document requiring their signature at the time of signing. (BPC § 9884.7(a)(3), CCR § 3353.1(a))
Written authorization consists of the customer’s signature and the date the customer authorized the repairs. (CCR § 3353.1(b))
Oral authorization consists of the date, time, name of the person authorizing the repairs, and telephone number called, if any. (CCR § 3353.1(c))
Electronic authorization consists of the date, time, name of the person authorizing the repairs, and email address or phone number (text messaging) contacted, if any. (CCR § 3353.1(d))
Documents supplementing the estimate to obtain a customer’s authorization, including but not limited to a series of electronic communications, such as emails or texts, between the automotive repair dealer and the customer, shall be uniquely identified and maintained as part of the same transaction. (CCR § 3353.1(e))
What is required in a work order?
A work order must contain the authorized estimate for a specific job, the repairs requested and authorized by the customer, and the vehicle’s odometer reading. (BPC § 9884.7(a)(2), CCR § 3352(b))
An automotive repair dealer engaged in mobile automotive repair must provide the customer a copy of the automotive repair dealer sign specified in CCR §§ 3351.3 and 3351.4 when providing a copy of the work order. (CCR §§ 3351.3, 3351.7.3(d))
Can the method of repair or parts listed in the work order be changed?
Yes, only if the customer authorizes the change in the method of repair or parts supplied prior to the change. (CCR § 3354(b))
Unusual circumstances and authorization
What are unusual circumstances?
Unusual circumstances are instances when the customer cannot deliver the vehicle to the automotive repair dealer for repairs during normal business hours or is not present when the vehicle is delivered. For example, the customer may have dropped off the vehicle at the facility before or after business hours and/or the vehicle may have been towed to the facility unaccompanied by the customer. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3353.2)
Learn more about towing fees and required authorization.
How are repairs authorized under unusual circumstances?
Before beginning any repairs, complete the following steps to obtain the customer’s authorization:
Prepare an estimate. (CCR § 3353.2(a))
Contact the customer by telephone, email, text, or other electronic means to provide all the information listed in the estimate and obtain the customer’s authorization. (CCR § 3353.2(b))
Properly document the customer’s authorization on both the estimate and invoice. (CCR § 3353.2(c))
Authorization is required before beginning any repairs, even when a vehicle is dropped off before or after normal business hours along with a note requesting repairs to be performed. The note does not constitute authorization.
Additional authorization
How are additional repairs authorized?
Before beginning any additional repairs beyond the original estimate, or having any additional charges accrue, complete the following steps: (BPC § 9884.9, CCR §§ 3353.1, 3354(a))
Prepare a revised work order that describes all additional parts and labor, provides the cost of all additional parts and labor, and includes the total revised cost.
Contact the customer by phone, email, text, or other electronic means to provide all the information listed in the revised work order and obtain the customer’s authorization.
Properly document the customer’s authorization on both the work order and invoice.
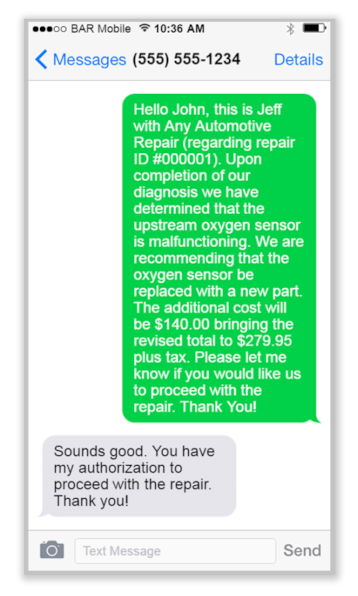
View a sample showing additional authorization obtained via text
Can the customer designate another person to authorize additional repairs?
Yes, the customer may designate another person to authorize any additional diagnosis, repairs, and/or parts at the time the initial authorization is provided. However, that person cannot be the automotive repair dealer, including an employee, agent, or person acting on their behalf, or an insurer involved in a claim involving repairs to the vehicle. (BPC § 9884.9(d), CCR § 3354(c)(2))
How is the customer’s designation documented?
Document the following information on either the work order or on a separate form:
The following title:
"DESIGNATION OF PERSON TO AUTHORIZE ADDITIONAL DIAGNOSIS, REPAIR, OR PARTS" (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(A))
The following statement:
"I hereby designate the individual named below to authorize any additional work not specified or parts not included in the original estimate for parts and labor." (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(B))
The name of the designated person (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(C))
The designated person’s contact information, such as telephone number and/or email address (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(D))
The customer’s signature (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(E))
The date of signing (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(F))
The work order number (CCR § 3354(c)(1)(G))
Towing fees and authorization
When must towing fees be disclosed?
If an automotive repair dealer provides or contracts for towing services, the towing fees must be provided to the customer before accepting payment for those services. (CCR § 3353(e))
Can towing fees be provided to the customer on a repair estimate?
No. Towing fees must be provided on a separate document, either electronic or printed. They may not be included on the repair estimate or invoice. (Vehicle Code §§ 22651.07(a)(3) and 22651.07(e), CCR § 3353(e))
How are towing fees authorized?
Customer authorization for towing fees must be on a separate form from any estimate and authorization for repairs. (Vehicle Code §§ 22651.07(a)(3) and 22651.07(e), CCR § 3353(e))
To learn more, see our guidance on towing and storage services.
Invoice
An invoice is a paper or electronic document provided to the customer upon completion of all repairs that contains the final price for parts and labor for a specific job. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3352(d))
Unless specified otherwise, all references to the invoice are intended for a ‘standard’ invoice.
When is the invoice provided to the customer?
The invoice is provided to the customer upon completion of all repairs for a specific job, including any preventative maintenance services defined in BPC § 9880.1(j). (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356)
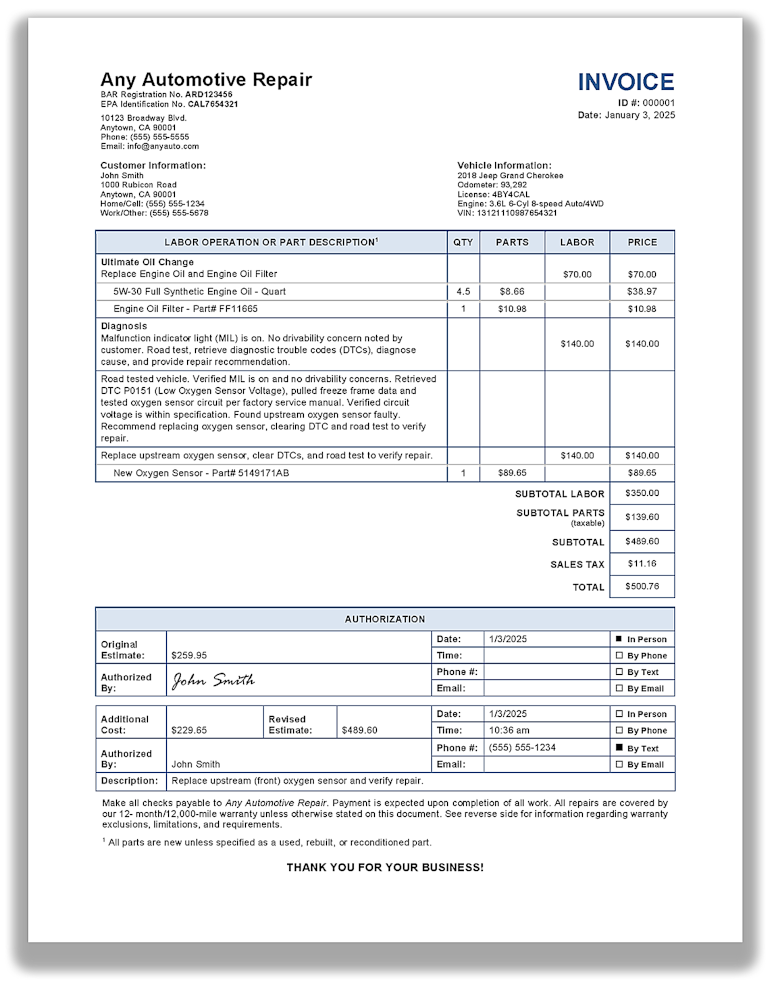
What is required in an invoice?
An invoice must contain the following:
Automotive repair dealer information: The automotive repair dealer registration number and the corresponding business name and address as shown in BAR’s records. (CCR § 3356(b))
Parts and labor:
An itemized list of all services and repairs performed and the prices for each. Include any diagnosis, warranty repairs, or repairs performed at no charge. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(1))
An itemized list of each part supplied. List each part in common terms so that the customer can understand what they purchased and the price of the part. State if each part is new, used, reconditioned, rebuilt, and whether any crash parts are OEM or non-OEM aftermarket. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(2))
A part kit may be listed as a single part if the brand name and corresponding part number is also provided. (CCR § 3356(c)(2))
Replaced parts that cannot be returned to the customer, if applicable. (CCR §§ 3355(c)(1)(B), 3356(i))
Prices/costs:
The subtotal price for all service and repair work performed. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(3))
The subtotal price for all parts supplied, not including sales tax. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(4))
The sales tax, if applicable. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(5))
The toxic waste fee charged, if any, as stated on the original estimate and the automotive repair dealer’s Environmental Protection Agency number. (CCR § 3357)
The total cost for all service and repair work, parts supplied, and applicable sales tax. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(c)(6))
Separate billing in an invoice for items generically noted as shop supplies, miscellaneous parts, fees for electronic communication with the Smog Check database, and the like, is prohibited. (CCR § 3356(g))
Authorization:
The customer’s declination of repair or reassembly after tear down, if applicable. (CCR §§ 3353(c)(3), 3356(h))
If customer authorization was provided under unusual circumstances, include the date and time of the authorization of the estimate, the name of the person who gave the authorization, and the telephone number or email address contacted to obtain the authorization. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(d))
If additional authorization was provided either orally or electronically, include the date and time of the additional authorization, the name of the person who authorized the additional repairs, the telephone number or email address contacted to obtain the additional authorization, a description of all additional parts and labor, the cost for additional parts and labor, and the total price for all repairs. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356(e))
Instead of detailing additional oral authorization on the invoice, the automotive repair dealer may obtain the customer’s signature or initials on an Acknowledgement of Notice and Consent, which must include the language below. When using the Acknowledgement of Notice and Consent, any revisions to the original estimate must be documented on the work order. (BPC § 9884.9(a)(2), CCR § 3356(e)(2))
"I acknowledge notice of oral approval of an increase in the original estimated price."
Is an invoice required for a no charge or warranty repair?
Yes, all parts supplied and all repairs performed by an automotive repair dealer, including all preventative maintenance services performed, any repairs performed at no charge, warranty repairs, and repairs paid for by the customer’s insurance company, must be recorded in an invoice provided to the customer. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356)
Are replaced parts required to be returned to the customer?
Yes, if requested by the customer at the time the estimate is authorized. However, core parts (such as a battery) that are sold on an exchange basis or parts that must be returned to the supplier under warranty are not required to be returned to the customer. In these circumstances, the customer must be offered the opportunity to inspect the replaced parts. Any replaced parts that cannot be returned to the customer must be recorded on the invoice. (BPC § 9884.10, CCR §§ 3355, 3356(i))
Are core charges on parts included in the invoice?
If a customer requests a replaced core part (such as a battery) that is sold on an exchange basis, the core charge may be included in the invoice. Note that core charges on parts do not apply to parts replaced under a warranty, which must be returned to the manufacturer. (BPC § 9884.10, CCR §§ 3355, 3356(i))
Can common industry-recognized acronyms be used when describing parts and labor in the estimate and invoice?
No, an estimate and invoice should itemize and describe all parts and labor for a specific job in a manner that the customer can easily understand what was purchased. The customer is not likely to understand that R&R means Remove and Replace, or that a TPS is a Throttle Position Sensor. (BPC §§ 9884.8, 9884.9, CCR §§ 3353, 3356)
If a mobile automotive repair business holds multiple automotive repair dealer registrations, must all registration numbers be included in the invoice?
No, only the automotive repair dealer registration number tied to the vehicle engaged in the specific job is required to be listed in the invoice. (CCR § 3356(b))
Can a lien sale be conducted if the customer fails to pay the invoice?
Yes, an automotive repair dealer may conduct a lien sale on a vehicle when the customer fails to pay the authorized cost for parts and labor. All invoice requirements must have been met to satisfy the lien sale, as required by Civil Code section 3068(a). (BPC § 9884.16)
Refer to Division 3, Part 4, Title 14, Chapter 6.5 of the Civil Code and www.dmv.ca.gov for applicable requirements related to lien sales.
Specialized invoices
What is required in a Smog Check invoice?
A Smog Check invoice must contain the same information that is required in a standard invoice. A copy of the Vehicle Inspection Report must be attached to the customer’s invoice. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR §§ 3340.41(a), 3356)
What is required in an automatic transmission invoice?
An automatic transmission invoice must contain the same information that is required in a standard invoice. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3356)
Using terms like exchanged, rebuilt, remanufactured, reconditioned, overhauled, or any expression of like meaning, to describe an automatic transmission in an estimate or invoice (or in any form of advertising), is permitted if all work specified in CCR § 3361.1(c) has been completed since the transmission was last used.
What is required in a windshield installation invoice?
A windshield installation invoice must contain the same information that is required in a standard invoice. It also must include the cure time, the date and time upon which the installation was completed, and whether the windshield is an OEM part or a non-OEM part. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR §§ 3356, 3365.1(c)(4))
What is required in an automotive air conditioning invoice?
An automotive air conditioning invoice must contain the same information that is required in a standard invoice. It also must include the high and low side system operating pressures, as applicable, and the center air distribution outlet temperature. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR §§ 3356, 3366(a)(15), 3366(a)(16))
When using terms like service, inspection, diagnosis, top off, performance check, or any expression of like meaning, to describe automotive air conditioning work in an estimate or invoice (or in any form of advertising), an automotive repair dealer must perform all procedures specified in CCR § 3366 as the accepted trade standards for air conditioning work.
What is required in a mobile automotive repair invoice?
A mobile automotive repair invoice must contain the same information that is required in a standard invoice. It also must include the address where the repairs were performed. If no physical address is available, include a description of the location. This could be a street and cross-street, a landmark, a mile-marker, or freeway on-ramp or off-ramp. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR §§ 3356, 3351.7.3(e)(1)-(2))
Sample documents
These documents are for sample purposes only. Example pricing, labor hours, and other details are included to show required information. The documents are not intended for actual use.
Estimate
Tear down estimate
Auto body/collision repair estimate
Repair estimate based on a third-party estimate

Automatic transmission diagnosis estimate
Automatic transmission tear down estimate
Work order
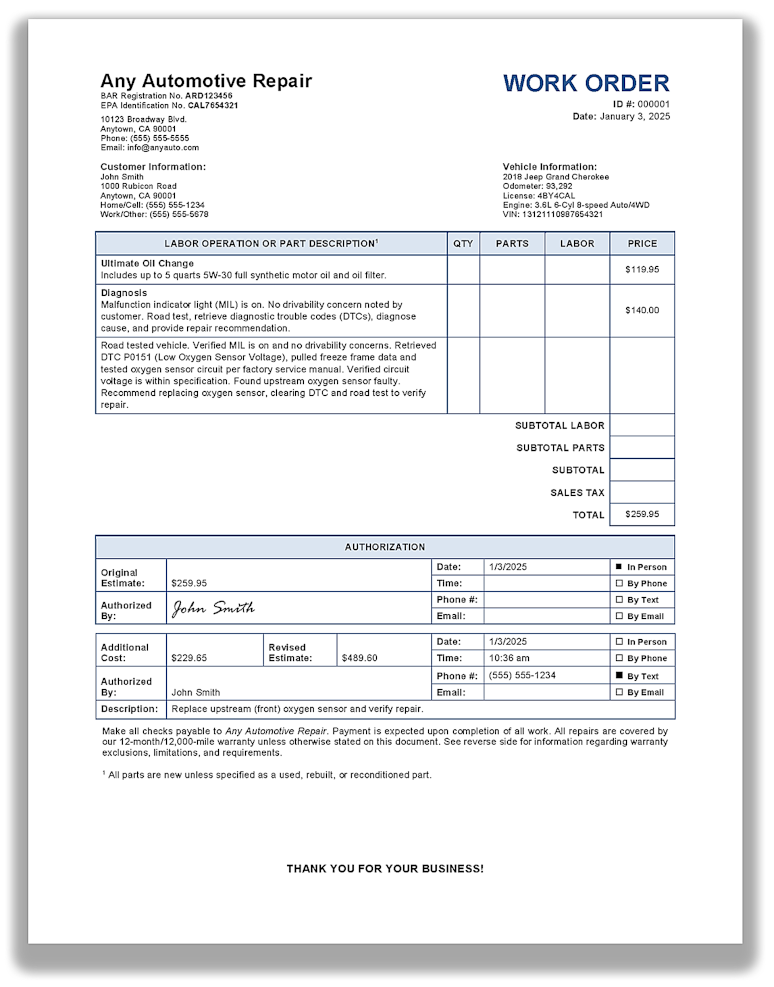
Additional authorization
The following sample shows additional authorization obtained via text.
Invoice
Maintenance of records
What records must be maintained by an automotive repair dealer?
The following records must be maintained in either written or electronic form:
All invoices (BPC § 9884.11, CCR § 3358(a))
All estimates, including all records, such as emails or texts, created to obtain the customer’s authorization (BPC § 9884.11, CCR § 3358(b))
All work orders, including all records supplementing the work order created to obtain additional authorization from the customer for any additional repairs estimated. (BPC § 9884.11, CCR § 3358(c))
If storing items electronically, remember to scan all documents that include a customer’s signature.
How long must records be maintained?
Records must be maintained for at least three years and shall be open for reasonable inspection and/or reproduction by BAR during normal business hours. (BPC § 9884.11, CCR §§ 3340.15(e), 3358(d))
Are records required to have a unique identifier?
Yes, all records associated with a specific transaction must have a unique identifier linking the records to that specific transaction. (CCR § 3358(e))
Business conduct
Automotive repair dealers are reminded that a registration may be denied, suspended, revoked, or placed on probation for acts or omissions related to business conduct including, but not limited to, the following: (BPC §§ 490, 9884.7)
Making untrue or misleading statements
Allowing a customer to sign a work order that does not state the repairs requested or the odometer reading
Failing to provide a customer a copy of a signed document
Fraud
Gross negligence
Failure to comply with the Automotive Repair Act or related regulations
Willful departure from, or disregard of accepted trade standards for good and workmanlike repair
Making false promises to get a customer to authorize a vehicle repair or service
Having repairs done by someone else without the knowledge or consent of the customer (unless documented that the customer cannot reasonably be notified)
Conviction of a violation of Penal Code section 551 (fraudulent acts)
Conviction of any crime substantially related to the qualifications of an automotive repair dealer
Definitions
Automotive repair dealer (ARD): a person who, for compensation, engages in the business of repairing or diagnosing malfunctions of motor vehicles, or engages in the business of collecting compensation for automotive repair services that are referred or sublet to someone other than the dealer or their employees. (BPC § 9880.1(a))
Repair of motor vehicles: all maintenance of and repairs to motor vehicles performed by an automotive repair dealer, excluding repairs made pursuant to a commercial business agreement and roadside services. (BPC § 9880.1(k))
Preventative maintenance services: includes oil and other fluid changes, rotating tires, and other services as defined in BPC § 9880.1(j).
Customer: the person presenting a motor vehicle for repair and authorizing the repairs to that motor vehicle. (BPC § 9880.1(f))
Third-party payor: an aftermarket warranty provider, insurer, or other entity who is responsible for, or has contracted with, the customer to provide payment for repairs to a vehicle. (CCR § 3303(w))
Crash part: a replacement for any of the non-mechanical sheet metal or plastic parts which generally constitute the exterior of a motor vehicle, including inner and outer panels. (CCR § 3303(o))
Original equipment manufacturer (OEM) crash part: a crash part made for or by the original vehicle manufacturer that manufactured, fabricated, or supplied a vehicle or a component part. (CCR § 3303(p))
Non-original equipment manufacturer (non-OEM) crash part: an aftermarket crash part not made for or by the manufacturer of the motor vehicle. (CCR § 3303(q))
Specific job: all the repair work to be performed in a single transaction, as listed on the estimate. This includes a description of each repair in terms the customer can understand. Descriptions must not include technical or industry terms. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3352(b))
Estimate: a paper or electronic document provided to the customer that contains an estimated price for parts and labor for a specific job. (BPC § 9884.9, CCR § 3352(a))
Tear down: the disassembly of a portion(s) or area(s) of the vehicle or vehicle component(s) in order to: (CCR § 3352(e))
Assess the extent of the damage
Evaluate the condition of the vehicle or vehicle component(s) in order to prepare an estimate.
A tear down is a repair and requires an estimate on the specific job to be performed.
Authorization: the customer’s consent for a specific job, expressed as either:
A written signature on the estimate authorizing a specific job. (CCR § 3352(f)(1))
A statement communicated either orally or electronically to the automotive repair dealer and documented on the estimate authorizing a specific job. (CCR § 3352(f)(2))
Electronic: relating to technology having electrical, digital, magnetic, wireless, optical, electromagnetic, or similar capabilities. (CCR § 3352(g))
Oral: voice communication, whether in person, by telephone, or by any electronic manner where voice can be heard. (CCR § 3352(h))
Work order: a paper or electronic document that contains the repairs requested by the customer, the estimate for a specific job, the customer's authorization of the estimate, and the vehicle’s odometer reading. (BPC § 9884.7(a)(2), CCR § 3352(c))
Invoice: a paper or electronic document provided to the customer upon completion of all repairs that contains the final price for parts and labor for a specific job. (BPC § 9884.8, CCR § 3352(d))
Request a presentation
BAR offers presentations on Write It Right, laws and regulations, and more. Presentations help you stay up to date on requirements for automotive repair dealers. They are also a great opportunity to ask questions and connect with a BAR representative. Request a presentation for your shop's next meeting or event.
Print this page
We recommend bookmarking this page for future reference. This ensures you have the most current information. If you choose to print, select Print from your browser menu or press:
Ctrl + P (Windows)
Command + P (MAC)
This page is print-friendly. Adjust your settings to improve the print quality, if needed.

